
This organisation was built with ❤️ by
Chanakya Ekbote, as a
part of the Cloud Native Computing Foundation during Google Summer of Code 2020,
with lots of amazing support from two of the best mentors in the world,
Paul Greenberg and
Yong Tang.
Overview
The ML Bridge organisation provides machine learning capabilities to languages and platforms that generally have a dearth of such capabilities. Moreover, one of the best features is that the components of the ML Bridge organisation are fully customizable, they can be tailored to fit the needs of any other project or organisation.
Currently, it is being used to integrate machine learning capabilities with CoreDNS, to protect people against malicious websites and applications. It helps in identifying websites that could be potentially used by malicious hackers and cybercriminals and prevents the user from accessing such websites.
Table of Contents
- Getting Started
- Approach
- The Inner Working of ML Bridge
- Important Links (Code)
- Code Documentation
- Contributing to the ML Bridge Organisation
- Acknowledgements
Getting Started
The repositories in the ML Bridge organisation require the capabilities of the Elasticsearch Server. To install the Elasticsearch Server please follow the instructions that can be found here.
For installing each component in the ML Bridge organisation please find the individual installation instructions in each individual repository. If you would to install the entire ML Bridge software suite, please follow the instructions given below the repository links. The links to each individual repository can be found below:
- The ML Bridge Plugin (A CoreDNS Plugin)
- The ML Bridge Middleware
- The ML Bridge User Interface
- The ML Bridge Machine Learning Module
To install and start CoreDNS please take a look at the CoreDNS
repository. Add the mlbridge plugin to
CoreDNS. To add external plugins, please take a look at the
example plugin.
The recommended file structure while cloning the repositories can be found below:
mlbridge
|__ mlbridge-machine-learning
|__ mlbridge-middleware
|__ mlbridge-ui
To create a new mlbridge directory and clone the repositories into that
directory, please use the following script:
mkdir mlbridge
cd mlbridge
git clone https://github.com/mlbridge/mlbridge-machine-learning.git
git clone https://github.com/mlbridge/mlbridge-middleware.git
git clone https://github.com/mlbridge/mlbridge-ui.git
To install the required Python dependencies, please use the following script:
cd mlbridge
pip install -r mlbridge-machine-learning/requirements.txt
pip install -r mlbridge-middleware/requirements.txt
pip install -r mlbridge-ui/requirements.txt
To start the ML Bridge software suite, first start the Elasticsearch Server. The instructions to start the same can be found here.
Next, start the CoreDNS Server. The CoreDNS can be started by following the instructions found here.
Then, go to the mlbridge directory by using the following command:
cd mlbridge
Finally, execute the following script to start the ML Bridge software suite:
python mlbridge-ui/mlbridge_ui/src/ui.py &
python mlbridge-middleware/mlbridge_middleware/src/middleware.py &
python mlbridge-machine-learning/python-code/training/py
Approach
General Overview
CoreDNS is a DNS Server written in Go. However, Go currently does not have native libraries for the interaction with the CUDA platform, which is essential for machine learning applications. At the same time, the Python ecosystem has tools like TensorFlow, PyTorch, MXNet and various others that not only interact with the CUDA platform but also allows for the easy prototyping and evaluation of deep learning models.
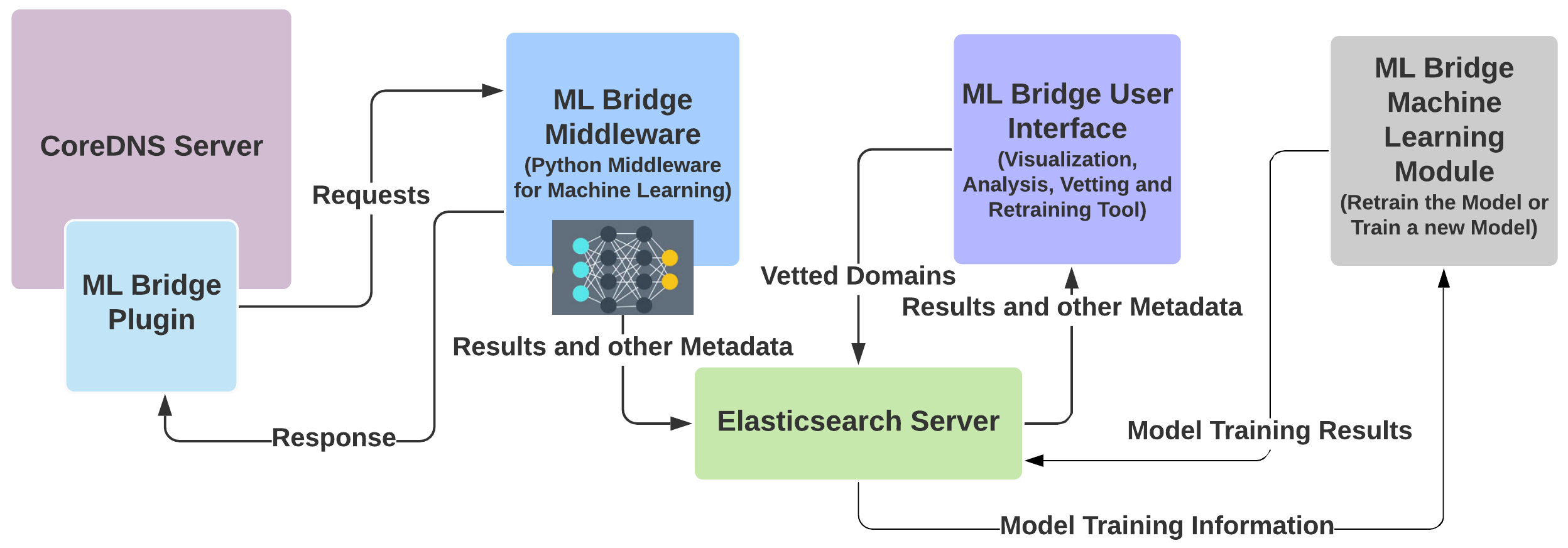
This project combines the deep learning capabilities that the Python ecosystem provides, with CoreDNS, by creating:
-
The ML Bridge Plugin (a CoreDNS Plugin): The plugin intercepts requests and forwards them to the Application Middleware for further processing. The repository for the ML Bridge Plugin can be found here.
-
The ML Bridge Middleware: The Middleware receives the request from the ML Bridge Plugin along with other metadata. The Middleware infers whether the request is from a malicious or a benign website, from a vetted list. However, if the domain is not in the vetted list, a machine learning model infers whether the request is malicious or benign, and then sends back a response to the plugin whether to allow the request or block it. It stores the result as well as other metadata to a database. The repository for the ML Bridge Middleware can be found here.
-
The ML Bridge User Interface: The user interface is used to analyse historical trends as to how many people are accessing malicious websites and at what frequency. It is also used to manually vet websites and classify them as malicious or benign. The user interface is also used to train new machine learning models or retrain existing models by communicating with the ML Bridge Machine Learning module. The repository for the ML Bridge User Interface can be found here.
-
The ML Bridge Machine Learning Module: The machine learning module is used to train new models or retrain existing ones. The module receives model training information from the details entered by the user in the Training section of the ML Bridge User Interface. The model is then trained according to the information entered, and then the results of the training are communicated back to the ML Bridge User Interface. The ML Bridge User Interface then displays the result in the form of accuracy and loss graphs as well as confusion matrices and metrics. The repository for the ML Bridge Machine Learning Module can be found here.
-
The Elasticsearch Server: The Elasticsearch Server acts as a communication channel between the different components of the ML Bridge Organisation. It is also used to store data locally, as and when required. To know more about the capabilities of the Elasticseach Server, please click here.
Machine Learning
Learning Dataset
The deep-learning model is trained on a COVID-19 Cyber Threat Coalition Blacklist for malicious domains (that can be found here) and on a list of benign domains from DomCop (that can be found here).
Currently, the pre-trained model has been trained on the top 500 domain names from both these datasets.
Learning Process
Data Preprocessing: Each domain name is converted to a unicode code point representation and then extended to a NumPy array of a length 256. The dataset was created by combining the malicious domains as well as the non-malicious. The dataset was split as follows:
- Train Set: 80% of the dataset.
- Validation Set: 10 % of the dataset
- Test Set: 10% of the dataset
Training: The deep-learning model is a Convolutional Neural Net that is trained using batch gradient descent with the Adam optimizer.
The Inner Working of ML Bridge
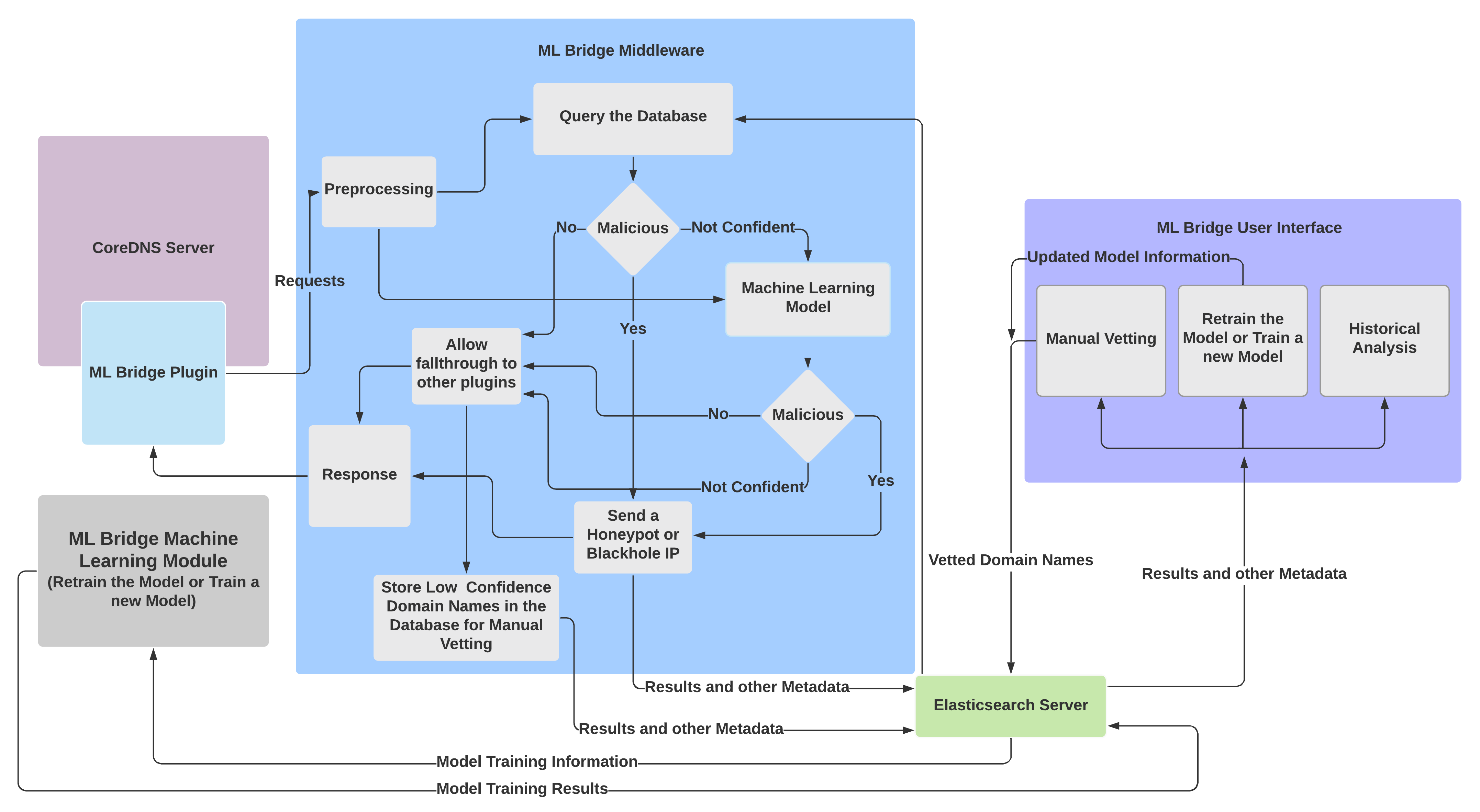
The ML Bridge Plugin
The ML Bridge Plugin is a CoreDNS plugin that forwards requests to the ML Bridge Middleware via HTTP POST requests. Once the Middleware processes the request, it sends back the prediction, whether the domain name is malicious or benign, to the plugin. Depending on the nature of the domain name, the plugin can be configured to allow the request to fall through to the other plugins or send the request to Honeypot or Blackhole IP addresses.
The ML Bridge Middleware
The Middleware is a Python Flask Server that contains the pre-trained Convolutional Neural Network. The Middleware receives the domain name queried as well as the IP addresses of the machine used to query that particular domain name, as a JSON message, via HTTP POST requests from the ML Bridge Plugin.
The Middleware first preprocesses the request forwarded from the Machine Learning Plugin. The preprocessed request is then cross checked against manually vetted lists. If the request is of a benign domain, a response is sent back to the ML Bridge Plugin that allows the fallthrough to other plugins. If the request is of a malicious domain, a response is sent back to the ML Bridge Plugin that prevents the fallthrough to other plugins. Moreover, the ML Bridge Plugin sends back Honeypot or Blackhole IP addresses to the user querying the malicious domain. If the domain does not exist in the manually vetted list, the preprocessed request is then sent to the machine learning model where it infers whether it is benign or malicious.
If the machine learning model is highly confident that the request is of a benign domain, then a response is sent back to the ML Bridge Plugin that allows the fallthrough to other plugins. If the model is highly confident that the domain name is malicious, a response is sent back to the ML Bridge Plugin that prevents the fallthrough to other plugins. Moreover, the ML Bridge Plugin sends back Honeypot or Blackhole IP addresses to the user querying the malicious domain. If the model is not confident about its prediction, then a response is sent back to the ML Bridge Plugin that allows the fallthrough to other plugins. However,the domain name is stored in the database for manual vetting.
The classification result as well, as other metadata such as the IP addresses, the date and time of the request, are stored in a NoSQL database, namely Elasticsearch, due to which storing and querying the classification result and the metadata is a fast process.
The TensorFlow Model
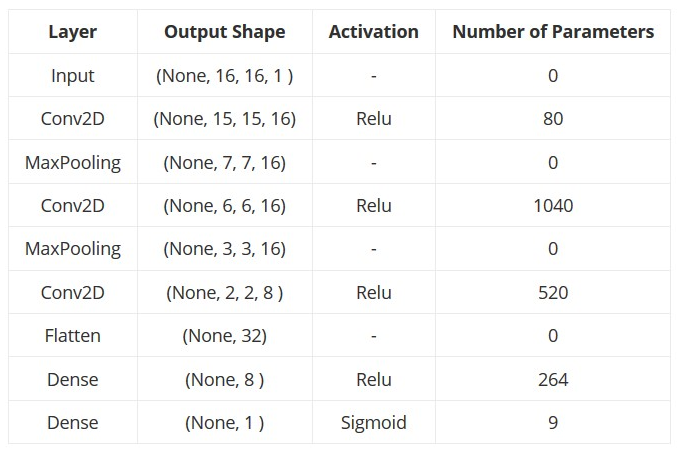
The default model that is used is a pre-trained Convolutional Neural Net whose input is a (16, 16, 1) shaped array and the output is a single value lying in between 0 and 1. If the output value is less than 0.5 the domain name is considered benign, else it is considered malicious.
The details of the Convolutional Neural Net are as follows:
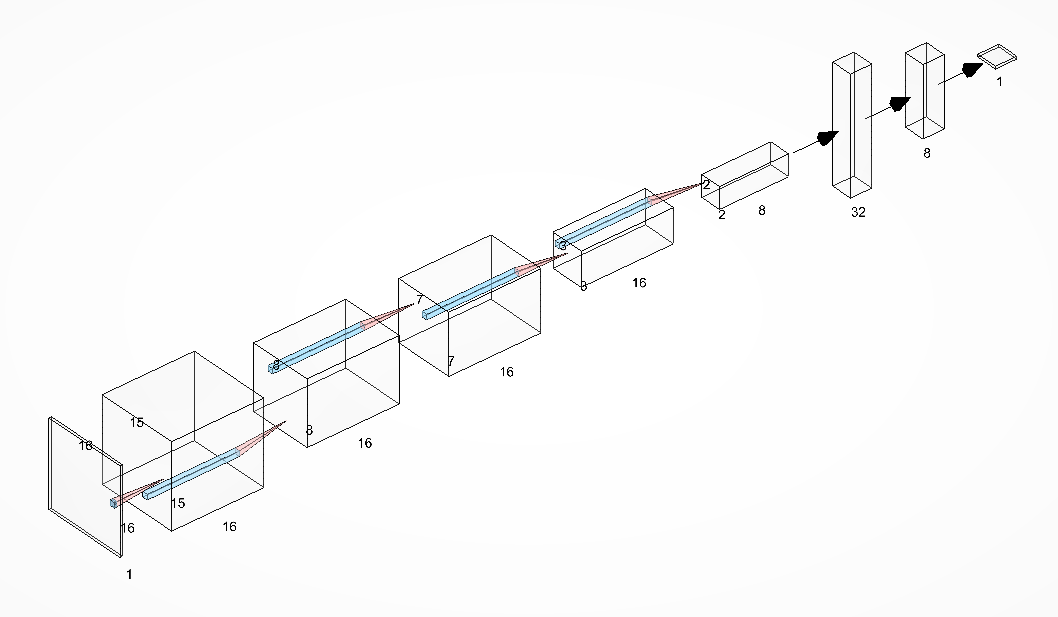
The Convolutional Neural Net can be visualized as follows:
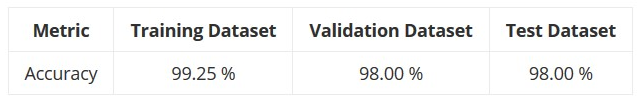
The Efficacy of the Trained Convolutional Neural Network
The accuracy for the Training Dataset, the Validation Dataset and Test Dataset is as follows:
Adding Your Own Model
To add your own model, you can either use the ML Bridge User Interface to train
a new model or you can train a model on your own without the ML Bridge User
Interface. If you use the ML Bridge User Interface to train the model will be
saved in the mlbridge/mlbridge-machine-learning/saved_models directory. If you
would like to create a model on your own then and then train it as you wish, you
are free to do so. Once the training is complete please save the model as:
your_model_name.hdf5 file in the
mlbridge/mlbridge-machine-learning/saved_models directory. For example: If
your model name is new_model, the name of the hdf5 file would be
new_model.hdf5. Next, go to the
mlbridge/mlbridge-middleware/mlbridge_middleware/src/middleware.py file and
then replace the dns_alert_model.hdf5 that can be found on this
line
with your_model_name.hdf5. For example: If your model name is new_model,
replace dns_alert_model.hdf5 with new_model.hdf5. Once this is complete,
rerun middleware.py and you’re good to go.
The ML Bridge User Interface
The ML Bridge User Interface has three main use cases:
- Historical Analysis
- Manual Vetting
- Training or Retraining Models
Historical Analysis
The application allows the user to historically analyse the frequency at which domains have been queried and the IP addresses of the users querying those domains.
The demo of the Historical Analysis can be found below:
The features of Historical Analysis are as follows:
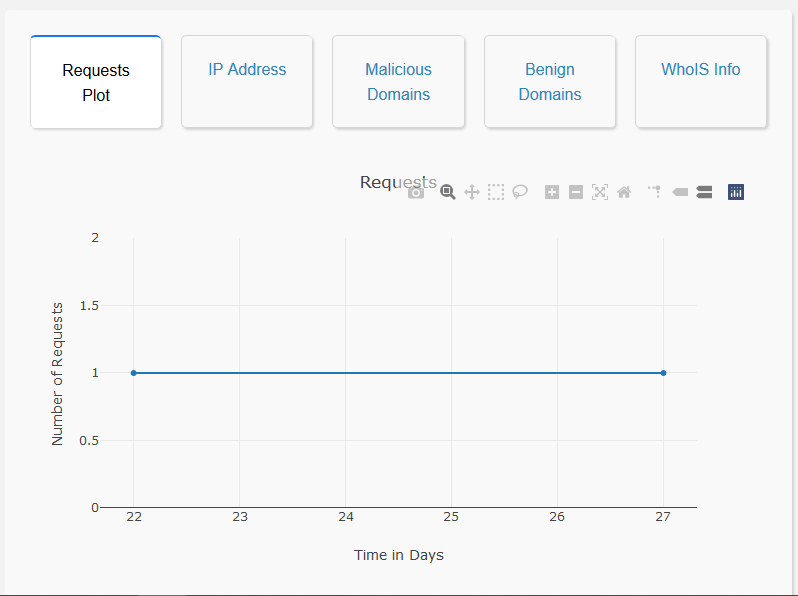
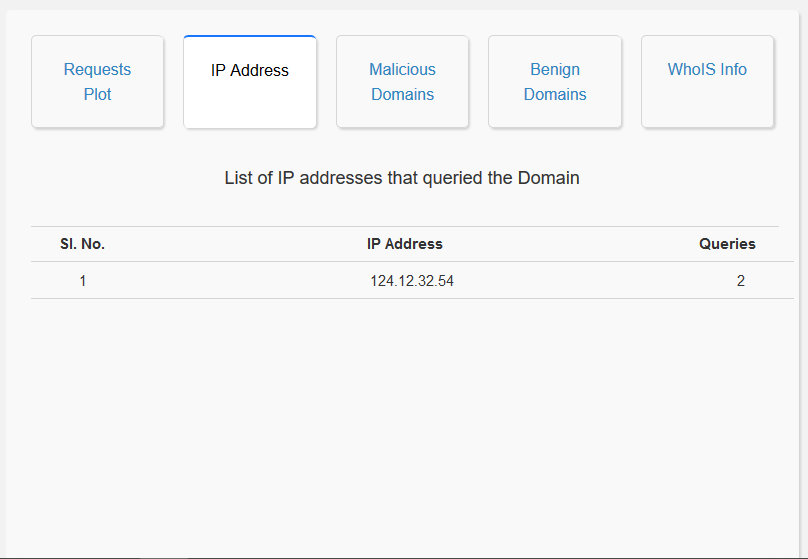
- Domain Name Analysis: The user interface enables the user to search for a particular domain name along with a time range. The user interface then searches for that particular domain name in the Elasticsearch database. Once the domain name is found, the user interface will display the number of requests to that particular domain name in that time range, the nature of the domain name (benign or malicious) and also the IP addresses that have queried that particular domain name. This allows for a domain specific analysis.
- Analysis of Malicious Domain Names: The user interface enables the user to visualize the top 20 malicious domains queried, as a bar graph. It also displays a list of all the malicious domains queried which can be seen via a toggle switch in the same window. This allows the user to gain a general picture of all the malicious domain names queried and also helps in identifying model misclassification. Moreover, the domain names that the model is not confident about, are highlighted in red.
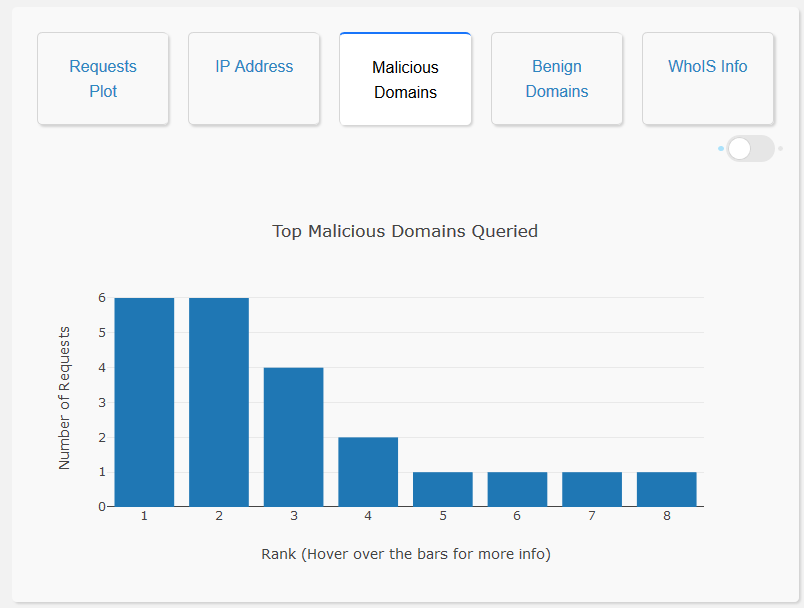
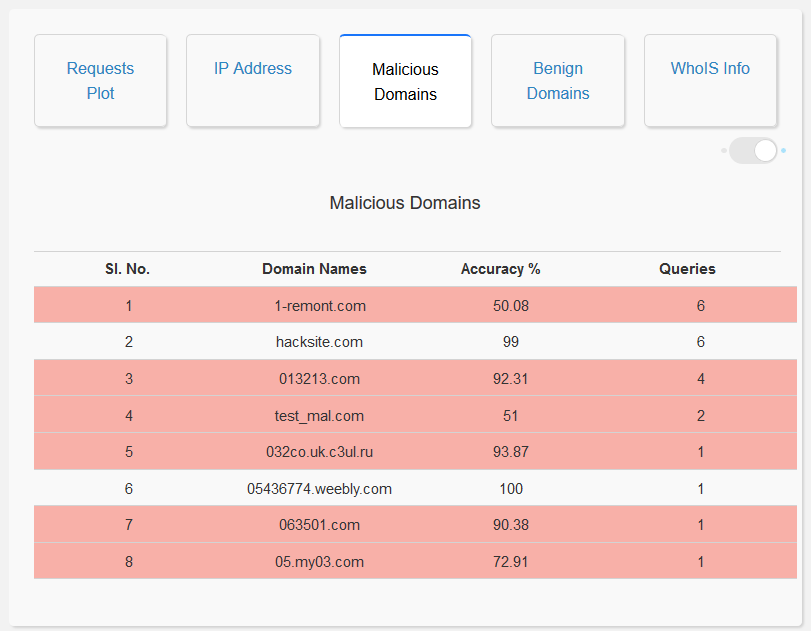
- Analysis of Benign Domain Names: The user interface enables the user to visualize the top 20 benign domains queried, as a bar graph. It also displays a list of all the benign domains queried which can be seen via a toggle switch in the same window. This allows the user to gain a general picture of all the benign domain names queried and also helps in identifying model misclassification. Moreover, the domain names that the model is not confident about, are highlighted in red.
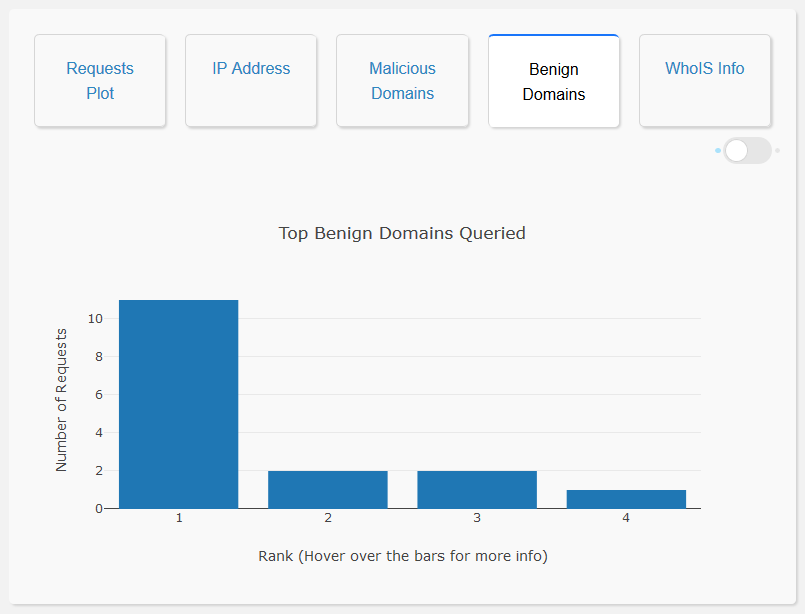
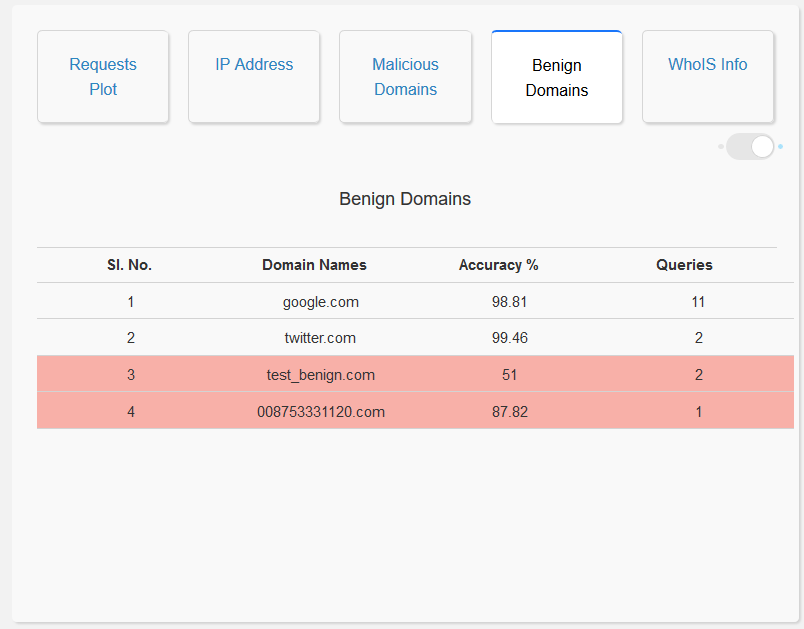
- WhoIS Information: The user interface enables the user to access the WhoIS records of the domain name. This allows the user to understand more information regarding the request queried, thereby enabling the user to make a well informed decision while vetting domain names.
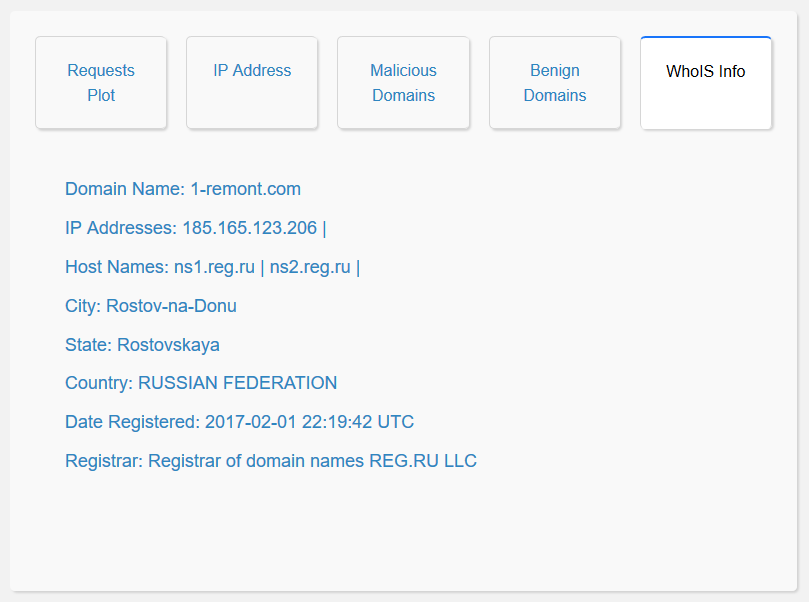
Manual Vetting
Manual Vetting allows the user to manually vet domain names that the model has low confidence in, thereby creating a new dataset of malicious or benign domains. This dataset can be used for blocking or allowing domains and also for updating the dataset for retraining the model.
The demo of Manual Vetting can be seen below:
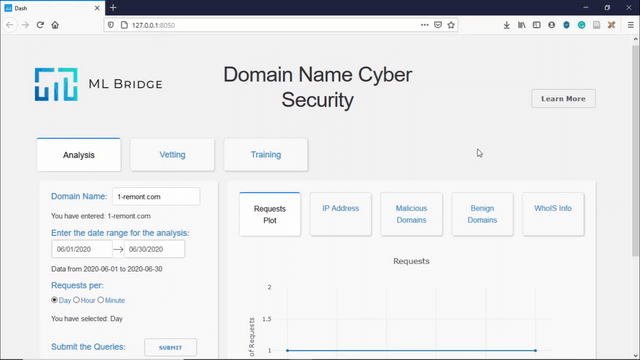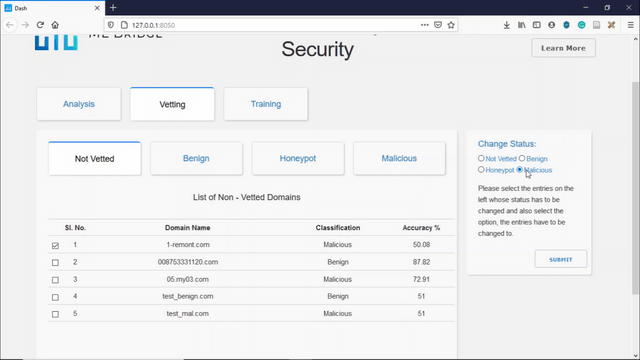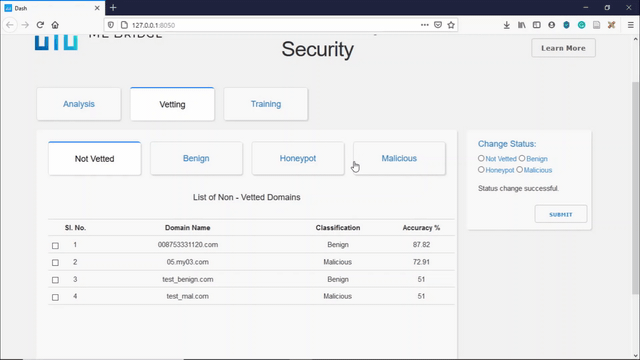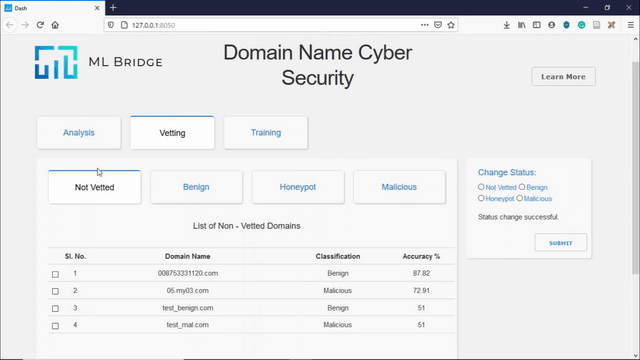
The user can decide whether to classify a non-vetted domain as a benign domain, or can be classified as a domain that is malicious or can be selected to send back Honeypot IP addresses to the malicious domain.
Training a new Model or Retraining older Models
The ML Bridge User Interface can be used to train new machine learning models or retrain older machine learning models. Such a capability is extremely useful when the current model underperforms or there is new data to train the model on.
A demo of the Training can be seen below:
The user has the ability to enter the number of epochs, the batch size as well
as the sample size for the model training. The loss as well as accuracy graphs
of the training are updated in real time. Once the training is completed, the
confusion matrices as well as confusion metrics can be observed to understand
the efficacy of the model. The model will be saved in the
mlbridge/mlbridge-machine-learning/saved_models directory.
The efficacy of older pre-trained models can also be observed by selecting the load model option and entering the name of a pre-trained model.
The ML Bridge Machine Learning Module
The ML Bridge Machine Learning Module is a module that uses the information as provided by the user regarding training, in the User Interface, namely the number of epochs, the batch size as well as the sample size to train a new model or retrain the existing model. The module then communicates back to the User Interface the accuracy graph, the loss graph, the confusion matrices as well as confusion metrics. A separate module such as the ML Bridge Machine Learning Module is used so that the training can be done parallelly while the user can use the User Interface for other purposes without having to wait for the training to complete.
The Elasticsearch Server
Elasticsearch is a NoSQL distributed database where the data is stored in a manner that data retrieval is quick. That makes it an ideal choice for communicating between four different ML Bridge components running parallelly.
Each component dumps data into the Elasticsearch Database, which then can be retrieved by other components, and then depending on the data, different actions can be taken by each component. Hence, it acts as an ideal communication channel. Moreover, it also helps in storing data that can be retrieved at a later time or date. For example, the model efficacy data continues to remain in the Elasticsearch Database (until the model is retrained, then the value gets updated). This helps in retrieving the model efficacy of a previously trained model, and helps in comparing the same with a newly trained model, and therefore changes in the results due to a change in the models can easily be identified.
Important Links (Code)
The links to the individual GitHub Repositories are as follows:
- The ML Bridge Plugin (A CoreDNS Plugin)
- The ML Bridge Middleware
- The ML Bridge User Interface
- The ML Bridge Machine Learning Module
Code Documentation
Please click on the individual links to obtain the documentation regarding the code for each repository:
Contributing to the ML Bridge Organisation
There are two main aspects of the ML Bridge Software Suite that we think need improvements:
-
Improving the ML Bridge Software Suite: Currently, customising the ML Bridge Software Suite to fit ones needs is not a very easy task. Hence, we would like to improve the overall code base to allow the users of the ML Bridge Software Suite to be able to customise it in a much easier fashion.
-
Improving the Domain Name Cybersecurity Project: There a few areas that, we think, can be improved upon in the Domain Name Cybersecurity Project:
- Improving The Machine Learning Module: The Machine Learning Module can be improved by using a larger dataset, or improving the overall machine learning model.
- Adding Other Models to Make the CoreDNS Server More Secure: Models such as the Homograph Detection Model can also be added to add an extra layer of security to the CoreDNS Server.
- Improving the User Interface: Any improvements to the ML Bridge User Interface, be it addition of new widgets to the User Interface or creating a desktop application using Electron, is more than welcome.
If you’d like to contribute to the ML Bridge Organisation with respect to the ideas listed above (or any idea for that matter), please raise an issue in the mlbridge.github.io repository. We’d love to discuss any improvements you have in mind 😃.
Acknowledgements
I would like to thank my mentors Paul Greenberg and Yong Tang for their continuous support and guidance throughout this amazing Google Summer of Code journey. They always ensured that all my doubts were cleared, helped me in identifying relevant issues and finding solutions for those problems, through extensive discussions. This journey would not have been possible without them. I would like to thank my friend Dheeraj who helped me design the ML Bridge logo. I would like to thank all the creators of the Dash Oil and Gas Project The Dash Oil and Gas Project was used as an inspiration for the ML Bridge User Interface. I would like to thank all the essential workers who are working tirelessly throughout this COVID-19 crisis. I would also like to thank Cloud Native Foundation (CNCF) as well as Google for providing me with this wonderful opportunity. I hope that both CNCF as well as Google through their respective student developer programs, continue to inspire many more developers for years to come and hope that their journey will be as memorable as mine 😄.